Health Library
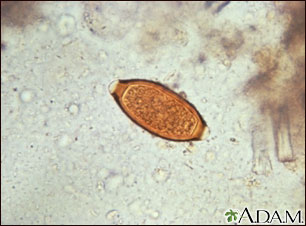
Whipworm infection
Intestinal parasite - whipworm; Trichuriasis; Round worm - trichuriasis
Whipworm infection is an infection of the large intestine with a type of roundworm.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Whipworm infection is caused by the roundworm Trichuris trichiura. It is a common infection that mainly affects children.
Children may become infected if they swallow soil contaminated with whipworm eggs. When the eggs hatch inside the body, the whipworm sticks inside the wall of the large intestine.
Whipworm is found throughout the world, especially in countries with warm, humid climates. Some outbreaks have been traced to contaminated vegetables (caused by soil contamination).
Symptoms
Most people who have whipworm infections don't have symptoms. Symptoms mainly occur in children, and range from mild to severe. A severe infection may cause:
- Bloody diarrhea
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Fecal incontinence (during sleep)
- Rectal prolapse (the rectum comes out of the anus)
Exams and Tests
A stool ova and parasites exam reveals the presence of whipworm eggs.
Treatment
The medicine albendazole is commonly prescribed when the infection causes symptoms. A different anti-worm medicine may also be prescribed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Full recovery is expected with treatment.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek medical attention if you or your child develop bloody diarrhea. In addition to whipworm, many other infections and illnesses can cause similar symptoms.
Prevention
Improved facilities for feces disposal have decreased the incidence of whipworm.
Always wash your hands before handling food. Teach your children to wash their hands, too. Thoroughly washing food may also help prevent this condition.
Related Information
DiarrheaRectal prolapse
Dehydration
Anemia
References
Diemert DJ. Nematode infections. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 327.
Dobbs KR, Dent AE. Trichuriasis (Trichuris trichiura). In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 339.
Mejia R, Weatherhead J, Hotez PJ. Intestinal nematodes (roundworms). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 286.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/10/2024
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 | A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
