Health Library
Fire ants
Fire ants are red-colored insects. A sting from a fire ant delivers a harmful substance, called venom, into your skin.
This article is for information only. DO NOT use it to treat or manage an actual fire ant sting. If you or someone you are with has an exposure, call the local emergency number (such as 911), or the local poison control center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Poisonous Ingredient
Fire ant venom contains a chemical called piperidine.
Where Found
Fire ants build dirt nests that form mounds, usually in open, grassy settings. They are typically found in the southern United States and other areas that do not freeze in winter.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a fire ant sting may include:
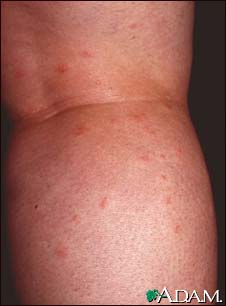
- Swelling, redness, itchiness, and pain around the site of the bite
- Pus-filled blisters that last 3 to 8 days
- Possible scab at the area of the bite that lasts 3 to 10 days
Those allergic to fire ant venom may also have:
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Throat swelling
Multiple fire ant stings may cause vomiting, diarrhea, swelling throughout the body, shortness of breath, low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, and shock.
Home Care
Home treatment depends on the location of, and reaction to, the sting.
Wash the exposed area with plenty of soap and water. DO NOT use alcohol to wash the area. Wash the eyes with plenty of water if any venom gets in them.
For mild stings, place ice (wrapped in a clean cloth) on the bite area for 10 minutes and then off for 10 minutes. Repeat this process. If the person has problems with blood circulation, decrease the time to prevent possible damage to the skin.
Some people are allergic to fire ant venom. If the reaction is severe, seek medical help right away and call your local emergency number (such as 911) or poison control.
Those who have an allergy to insect bites or stings should carry a bee sting kit and know how to use it in an emergency. These kits require a prescription.
Before Calling Emergency
Have this information ready:
- Person's age, weight, and condition
- The type of insect, if possible
- Time of the bite
Poison Control
Your local poison control center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States. This national hotline will let you talk to experts in poisoning. They will give you further instructions.
This is a free and confidential service. All local poison control centers in the United States use this national number. You should call if you have any questions about poisoning or poison prevention. It does NOT need to be an emergency. You can call for any reason, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
What to Expect at the Emergency Room
The health care provider will measure and monitor the person's vital signs, including temperature, pulse, breathing rate, and blood pressure. The wound will be treated as appropriate.
The person may receive:
- Blood and urine tests
- Breathing support, including oxygen (severe allergic reactions may require a tube down the throat and breathing machine)
- ECG (electrocardiogram, or heart tracing)
- Intravenous fluids (IV, through a vein)
- Medicines to treat symptoms
Outlook (Prognosis)
The sooner appropriate treatment is started, the better the outcome. People who are not allergic to fire ants should be fine in a few hours to a few days. People with severe allergic reactions may need to stay in the hospital.
References
Buttaravoli PM, Leffler S, Herrington RR. Fire ant stings. In: Buttaravoli PM, Leffler S, Herrington RR, eds. Minor Emergencies. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 169.
Elston DM. Bites and stings. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 85.
Erickson TB, Márquez A. Arthropod envenomation and parasitism. In: Auerbach PS, Cushing TA, Harris NS, eds. Auerbach's Wilderness Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 41.
Curtis AM, Erickson TB. Venomous animal injuries. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 53.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 7/1/2023
Reviewed By: Jesse Borke, MD, CPE, FAAEM, FACEP, Attending Physician at Kaiser Permanente, Orange County, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 | A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
