Health Library
Chemosis
Fluid-filled conjunctiva; Swollen eye or conjunctiva
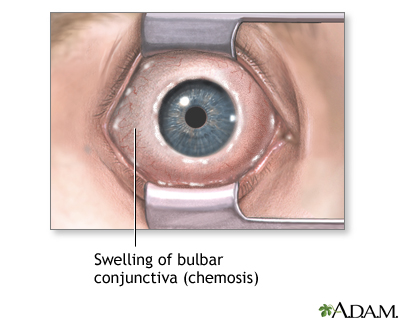
Chemosis is swelling of the tissue that lines the eyelids and surface of the eye (conjunctiva).
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Considerations
Chemosis is a sign of eye irritation. The outer surface of the eye (conjunctiva) may look like a big blister. It can also look like it has fluid in it. When severe, the tissue swells so much that you can't close your eyes properly.
Chemosis is often related to allergies or an eye infection. Chemosis can also be a complication of eye surgery, or it may occur from rubbing the eye too much.
Causes
Causes may include:
- Angioedema
- Allergic reaction
- Bacterial infection (conjunctivitis)
- Viral infection (conjunctivitis)
Home Care
Over-the-counter antihistamines and cool compresses placed on the closed eyes may help with symptoms due to allergies.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if:
- Your symptoms do not go away.
- You can't close your eye all the way.
- You have other symptoms, such as eye pain, change in vision, difficulty breathing, or fainting.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your symptoms, which may include:
- When did it start?
- How long does the swelling last?
- How bad is the swelling?
- How much is the eye swollen?
- What, if anything, makes it better or worse?
- What other symptoms do you have? (For example, breathing problems)
Your provider may prescribe eye medicine to reduce swelling and treat any conditions that may be causing the chemosis.
Related Information
AllergiesReferences
Fernandez A, Asbell P, Roy N. Emerging therapies targeting eosinophil-mediated inflammation in chronic allergic conjunctivitis. Ocul Surf. 2022;26:191-196. PMID: 35970432 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35970432/.
Kumar NM, Barnes SD, Pavan-Langston D, Azar DT. Microbial conjunctivitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 112.
McNab AA. Orbital infection and inflammation. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 12.14.
Rubenstein JB, Kelly E. Infectious conjunctivitis. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 4.6.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 5/10/2023
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 | A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
