Health Library
Fontanelles - enlarged
Soft spot - large; Newborn care - enlarged fontanelle; Neonatal care - enlarged fontanelle
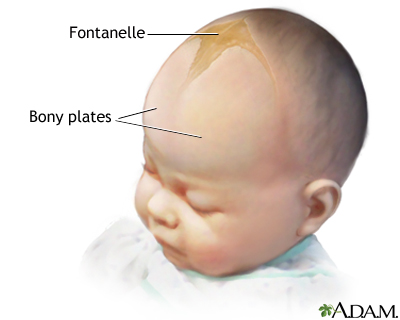
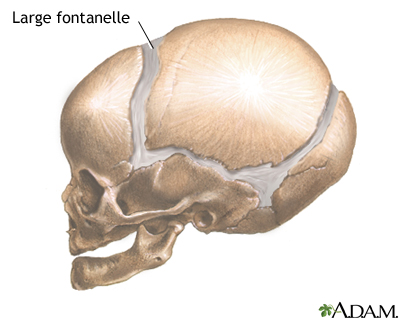
Enlarged fontanelles are larger than expected soft spots in the head for the age of a baby.
The skull of an infant or young child is made up of bony plates that allow for growth of the skull. The borders at which these plates intersect are called sutures or suture lines. The spaces where these connect, but are not completely joined, are called soft spots or fontanelles (fontanel or fonticulus).
Images


I Would Like to Learn About:
Considerations
Fontanelles allow for growth of the skull during an infant's first year. Slow or incomplete closure of the skull bones is most often the cause of a wide fontanelle.
Causes
Larger than normal fontanelles are most commonly caused by:
- Down syndrome
- Hydrocephalus
- Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR)
- Premature birth
Rarer causes:
- Achondroplasia
- Apert syndrome
- Cleidocranial dysostosis
- Congenital rubella
- Neonatal hypothyroidism
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Rickets
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you think that the fontanelles on your baby's head are larger than they should be, talk to your health care provider. Most of the time, this sign will have been seen during the baby's first medical exam.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
An enlarged large fontanelle is almost always found by the provider during a physical exam.
- The provider will examine the child and measure the child's head around the largest area.
- The provider may also turn off the lights and shine a bright light over the child's head.
- Your baby's soft spot will be regularly checked at each well-child visit.
Blood tests and imaging tests of the head may be done.
Related Information
Cranial suturesAnterior
Fontanelles - sunken
Fontanelles - bulging
References
Kinsman SL, Johnston MV. Congenital anomalies of the central nervous system. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 609.
Piña-Garza JE, James KC. Disorders of cranial volume and shape. In: Piña-Garza JE, James KC, eds. Fenichel's Clinical Pediatric Neurology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 18.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/6/2023
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 | A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
