Health Library
Feeding tube - infants
Gavage tube - infants; OG - infants; NG - infants
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Information
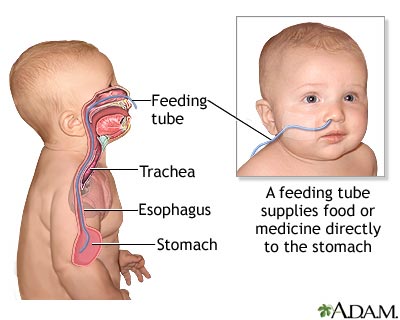
A feeding tube is a small, soft, plastic tube placed through the nose (NG) or mouth (OG) into the stomach. These tubes are used to provide feedings and medicines into the stomach until the baby can take food by mouth.
WHY IS A FEEDING TUBE USED?
Feeding from the breast or bottle requires strength and coordination. Sick or premature babies may not be able to suck or swallow well enough to bottle or breastfeed. Tube feedings allow the baby to get some or all of their feeding into the stomach. This is the most efficient and safest way to provide good nutrition. Oral medicines can also be given through the tube.
HOW IS A FEEDING TUBE PLACED?
A feeding tube is gently placed through the nose or mouth into the stomach. An x-ray can confirm correct placement. In babies with feeding problems, the tip of the tube may be placed past the stomach into the small intestine. This provides slower, continuous feedings.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS OF A FEEDING TUBE?
Feeding tubes are generally very safe and effective. However, problems may occur, even when the tube is placed properly. These include:
- Irritation of the nose, mouth, or stomach, causing minor bleeding
- Stuffy nose or infection of the nose if the tube is placed through the nose
If the tube is misplaced and not in the proper position, the baby may have problems with:
- An abnormally slow heart rate (bradycardia)
- Breathing
- Spitting up
In rare cases, the feeding tube can puncture the stomach.
References
George DE, Ogholikhan S. Tubes for enteric access. In: Wyllie R, Hyams JS, Kay M, eds. Pediatric Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 87.
Poindexter BB, Martin CR. Nutritional support for the preterm infant. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 42.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 4/1/2024
Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 | A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
