Health Library
Ear surgery - series
Normal anatomy
This image demonstrates normal appearance of the ears in relation to the face.
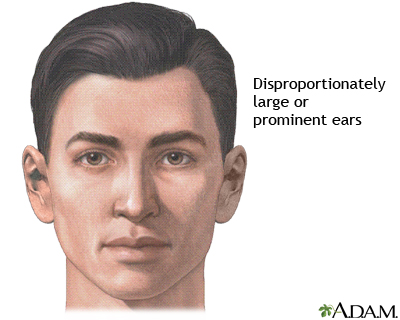
Indication
Ear surgery may be performed to set disproportionately large or prominent ears closer to the head.

Procedure
Thousands of ear surgeries (otoplasties) are performed successfully each year. The surgery may be done in the surgeon's office-based facility, in an outpatient surgical facility, or in a hospital. The surgery is performed while the patient is awake but pain free (local anesthetic) or deep asleep and pain free (general anesthetic). The procedure usually lasts about two hours, depending on the extent of the correction needed.
The most commonly employed technique is one in which the surgeon makes incisions in the back of the ear and removes skin to expose the ear cartilage. Sutures are used to fold the cartilage to reshape the ear.
Other surgeons choose to forgo sutures in favor of cutting or abrading the cartilage before folding it.
The ear is brought closer to the head by creating a more pronounced fold (called the antihelix) in the central portion of the ear.

Aftercare
The ears are covered with a bulky, moderate pressure dressing following surgery. There is usually some tenderness and discomfort, that is easily controlled by medication. Most patients leave the hospital on the same day, or shortly thereafter.
Within two to four days, the outer pressure dressings are removed but the patient is asked to wear a light head dressing for two to three weeks to promote healing.
Faint scars are concealed in the flexion creases behind the ears; there are no incisions in front of the ears.
Related Information
Cosmetic ear surgeryBACK TO TOP
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Tang Ho, MD, Associate Professor, Division of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, The University of Texas Medical School at Houston, Houston, TX. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 | A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
