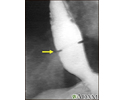
Lower esophageal ring
Esophagogastric ring; Schatzki's ring; Dysphagia - esophageal ring; Swallowing problems - esophageal ring
A lower esophageal ring is an abnormal ring of tissue that forms where the esophagus (the tube from the mouth to the stomach) and stomach meet.
Causes
A lower esophageal ring is a narrowing of the esophagus that occurs in a small number of people. The cause of the problem is unclear, but many believe that it is caused by acid reflux.
Narrowing of the esophagus may also be caused by:
- Injury
- Tumors
- Esophageal stricture
Symptoms
For most people, a lower esophageal ring does not cause symptoms.
The most common symptom is the feeling that food (especially solid food) is stuck in the lower neck or under the breastbone (sternum).
Exams and Tests
Tests that show the lower esophageal ring include:
- EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)
- Barium swallow (x-ray with barium)
Treatment
A device called a dilator is passed through the narrowed area to stretch the ring. Sometimes, a balloon is placed in the area and inflated, to help widen (dilate) the ring.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Swallowing problems may return. You may need repeat treatment.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have swallowing problems.
References
DeVault KR. Symptoms of esophageal disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 13.
Madanick RD, Kaila V. Anatomy, histology, embryology, and developmental anomalies of the esophagus. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 43.
Review Date: 10/31/2022