Enteritis
Enteritis is inflammation of the small intestine.
Enteritis is most often caused by eating or drinking things that are contaminated with bacteria or viruses. The germs settle in the small intestine and cause inflammation and swelling.
Enteritis may also be caused by:
- An autoimmune condition, such as Crohn disease
- Certain medicines, including NSAIDS (such as ibuprofen and naproxen sodium) and cocaine
- Damage from radiation therapy
- Celiac disease
- Tropical sprue
- Whipple disease
The inflammation can also involve the stomach (gastritis) and large intestine (colitis).
Risk factors include:
- Recent stomach flu among household members
- Recent travel
- Exposure to unclean water
Types of enteritis include:
- Bacterial gastroenteritis
- Campylobacter enteritis
- E coli enteritis
- Food poisoning
- Radiation enteritis
- Salmonella enteritis
- Shigella enteritis
- Staph aureus food poisoning
- Non-bacterial infections such as viruses and protozoa
Symptoms
The symptoms may begin hours to days after you become infected. Symptoms may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea -- acute and severe
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Blood in the stool
Exams and Tests
Tests may include:
- A stool culture culture or multiplex PCR to look for the type of infection. However, this test may not always identify the bacteria or other organisms causing the illness.
- A colonoscopy and/or upper endoscopy to look at the small intestine and to take tissue samples if needed.
- Imaging tests, such as CT scan and MRI, if symptoms persist.
Treatment
Mild cases of enteritis often do not need testing or treatment.
Antidiarrheal medicine is sometimes used.
You may need rehydration with electrolyte solutions if your body does not have enough fluids.
You may need medical care and fluids through a vein (intravenous fluids) if you have diarrhea and cannot keep fluids down. This is often the case with young children.
If you take diuretics (water pills) or an ACE inhibitor and develop diarrhea, you may need to stop taking the medicines. However, do not stop taking any medicine without first talking to your health care provider.
You may need to take antibiotics.
People who have Crohn disease will often need to take anti-inflammatory medicines (not NSAIDs).
Outlook (Prognosis)
Symptoms most often go away without treatment in a few days in otherwise healthy people.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Dehydration
- Long-term diarrhea
Note: In babies, the diarrhea can cause severe dehydration that comes on very quickly.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You become dehydrated.
- Diarrhea does not go away in 3 to 4 days.
- You have a fever over 101°F (38.3°C).
- You have blood in your stool
- You have severe belly pain
Prevention
The following steps may help prevent enteritis:
- Always wash your hands after using the toilet and before eating or preparing food or drinks. You may also clean your hands with an alcohol-based product containing at least 60% alcohol.
- Boil water that comes from unknown sources, such as streams and outdoor wells, before drinking it.
- Use only clean utensils for eating or handling foods, particularly when handling eggs and poultry.
- Cook food thoroughly.
- Use coolers to store food that needs to stay chilled.
References
Fleckenstein JM. Approach to the patient with suspected enteric infection. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 262.
Lima AAM, Warren CA, Guerrant RL. Acute dysentery syndromes (diarrhea with fever). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 99.
Melia JMP, Sears CL. Infectious enteritis and proctocolitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 110.
Semrad CE. Approach to the patient with diarrhea and malabsorption. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 126.
Salmonella typhi organism - illustration
Salmonella typhi organism
illustration
Yersinia enterocolitica organism - illustration
Yersinia enterocolitica organism
illustration
Campylobacter jejuni organism - illustration
Campylobacter jejuni organism
illustration
Clostridium difficile organism - illustration
Clostridium difficile organism
illustration
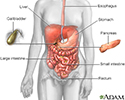
Digestive system - illustration
Digestive system
illustration
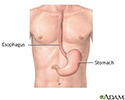
Esophagus and stomach anatomy - illustration
Esophagus and stomach anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 6/11/2024