Paraphimosis
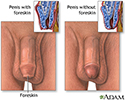
Paraphimosis occurs when the foreskin of an uncircumcised male cannot be pulled back over the head of the penis.
Causes of paraphimosis include:
- Injury to the penis.
- Failure to return the foreskin to its normal location after urination or washing. This is more common in hospitals and nursing homes.
- Infection, which may be due to not washing the area well.
Men who have not been circumcised and those who may not have been correctly circumcised are at risk.
Paraphimosis occurs most often in boys and older men.
Symptoms
The foreskin is pulled back (retracted) behind the rounded tip of the penis (glans) and stays there. The retracted foreskin and glans become swollen. This makes it difficult to return the foreskin to its extended position.
Symptoms include:
- Inability to pull the retracted foreskin forward over the head of the penis
- Painful swelling at the end of the penis
- Pain in the penis
Exams and Tests
A physical exam confirms the diagnosis. The health care provider will usually find a "doughnut" around the shaft near the head of the penis (glans).
Treatment
Pressing on the head of the penis while pushing the foreskin forward may reduce the swelling. If this fails, prompt surgical circumcision or other surgery to relieve swelling will be needed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is likely to be excellent if the condition is diagnosed and treated quickly.
Possible Complications
If paraphimosis is left untreated, it can disrupt blood flow to the tip of the penis. In extreme (and rare) cases, this may lead to:
- Damage to the penis tip
- Gangrene
- Loss of the penis tip
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to your local emergency room if this occurs.
Prevention
Returning the foreskin to its normal position after pulling it back may help prevent this condition.
Circumcision, when done correctly, prevents this condition.
References
Boswell B, Thomas AA. Pediatric genitourinary and renal tract disorders. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 168.
Elder JS. Anomalies of the penis and urethra. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 559.
Virasoro R, Jordan GH, McCammon KA. Surgery for benign disorders of the penis and urethra. In: Partin AW, Domochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 82.
Review Date: 1/1/2023