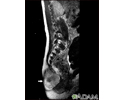
Malignant teratoma of the mediastinum
Dermoid cyst - malignant; Nonseminomatous germ cell tumor - teratoma; Immature teratoma; GCTs - teratoma; Teratoma - extragonadal
A teratoma is a type of tumor that contains one or more of the three layers of cells found in a developing baby (embryo). These cells are called germ cells. A teratoma is one type of germ cell tumor that can be benign or cancerous.
The mediastinum is located inside the front of the chest in the area that separates the lungs. The heart, large blood vessels, windpipe, thymus gland, lymph nodes and esophagus are found there.
Causes
Malignant mediastinal teratoma occurs most often in young men in their 20s or 30s. Most malignant teratomas can spread throughout the body, and have spread by the time of diagnosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Chest pain or pressure
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Limited ability to tolerate exercise
- Reduced exercise tolerance
- Shortness of breath
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about the symptoms. The exam may reveal a blockage of the veins entering the center of the chest due to increased pressure in the chest area.
The following tests help diagnose the tumor:
- Chest x-ray
- CT, MRI, or PET scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis
- Nuclear imaging to look for cancer that has spread to other parts of the body
- Blood tests to check beta-HCG, alpha fetoprotein (AFP), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels
- Mediastinoscopy with biopsy
Treatment
Surgical removal is the mainstay of treatment.
Chemotherapy is used to treat the immature teratoma. A combination of medicines (usually cisplatin, etoposide, and ifosfamide) is commonly used.
After chemotherapy is complete, CT scans are done again to see if any of the tumor remains. Surgery may be recommended if there is a risk that the cancer will grow back in that area or if any cancer has been left behind.
Support Groups
There are many support groups available for people with cancer.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook depends on:
- The size and location of the tumor
- The person's age
- Whether the cancer has spread to other organs
Possible Complications
The cancer can spread throughout the body and there may be complications of surgery or related to chemotherapy.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of malignant teratoma.
References
Triplette M, Varghese TK, Cheng G-S. Mediastinal tumors and cysts. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 115.
Wald O, Izhar U, Sugarbaker DJ. Lung, chest wall, pleura, and mediastinum. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 58.
Review Date: 7/29/2024