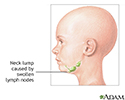
Neck lump
Lump in the neck
A neck lump is any lump, bump, or swelling in the neck.
Considerations
There are many causes of lumps in the neck. The most common lumps or swellings are enlarged lymph nodes. These can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, cancer (malignancy), or other rare causes.
Swollen salivary glands under the jaw may be caused by infection or cancer. Lumps in the muscles of the neck are caused by injury or spasm of the neck muscles (torticollis). These lumps are often at the front of the neck. Lumps in the skin or just below the skin are often caused by cysts, such as sebaceous cysts.
The thyroid gland may also produce swelling or one or more lumps. This can be due to thyroid disease or cancer. Most cancers of the thyroid gland grow very slowly. They are often cured with surgery, even if they have been present for several years.
All neck lumps in children and adults should be checked right away by a health care provider. In children, most neck lumps are caused by infections that can be treated. Treatment should start quickly to prevent complications or the spread of infection.
As adults age, the likelihood of the lump being a cancer increases. This is particularly true for people who smoke or drink a lot of alcohol. Most lumps in adults are not cancers.
Causes
Lumps in the neck from swollen lymph nodes may be caused by:
- Bacterial or viral infection
- Cancer
- Thyroid disease
- Allergic reaction
Lumps in the neck due to enlarged salivary glands may be caused by:
- Infection
- Mumps
- Salivary gland tumor
- Stone in salivary duct
Home Care
See your provider to have the cause of the neck lump diagnosed and treated.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have an abnormal neck swelling or lumps in your neck.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will take your medical history and do a physical exam.
You may be asked questions such as:
- Where is the lump located?
- Is it a hard lump or a soft, pliable (moves slightly), bag-like (cystic) mass?
- Is it painless?
- Is the entire neck swollen?
- Has it been growing bigger? Over how many months?
- Do you have a rash or other symptoms?
- Do you have difficulty breathing?
If you are diagnosed with a goiter (thyroid gland enlargement), you may need to take medicine or have surgery to remove it.
You may need the following tests if the provider suspects a thyroid nodule or another abnormality in the neck:
- Ultrasound scan of the thyroid and neck tissues
- CT scan of the head or neck
- Radioactive thyroid scan
- Thyroid biopsy
- Lymph node biopsy
If the lump is caused by a bacterial infection, you may need to take antibiotics. If the cause is a noncancerous mass or cyst, you may need surgery to remove it.
References
Bell EB, Nugent A, El-Deiry MW. Differential diagnosis of neck masses. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 113.
Matlock AG, Pfaff JA. Otolaryngology. In: Walls RM. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 58.
Review Date: 2/2/2023