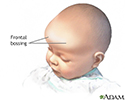
Frontal bossing
Frontal bossing is an unusually prominent forehead. It is sometimes associated with a heavier than normal brow ridge.
Frontal bossing is seen only in a few rare syndromes, including acromegaly, a long-term (chronic) disorder caused by too much growth hormone, which leads to enlargement of the bones of the face, jaw, hands, feet, and skull.
Causes
Causes include:
- Acromegaly
- Basal cell nevus syndrome
- Congenital syphilis
- Cleidocranial dysostosis
- Crouzon syndrome
- Hurler syndrome
- Pfeiffer syndrome
- Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
- Russell-Silver syndrome (Russell-Silver dwarf)
- Use of the antiseizure drug trimethadione during pregnancy
Home Care
There is no home care needed for frontal bossing. Home care for disorders associated with frontal bossing varies with the specific disorder.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you notice that your child's forehead looks overly prominent, talk to your health care provider.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
An infant or child with frontal bossing generally has other symptoms and signs. Taken together, these define a specific syndrome or condition. The diagnosis is based on a family history, medical history, and thorough physical evaluation.
Medical history questions documenting frontal bossing in detail may include:
- When did you first notice the problem?
- What other symptoms are present?
- Have you noticed any other unusual physical characteristics?
- Has a disorder been identified as the cause of the frontal bossing?
- If so, what was the diagnosis?
Lab studies may be ordered to confirm the presence of a suspected disorder.
References
Kinsman SL, Johnston MV. Congenital anomalies of the central nervous system. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 609.
Michaels MG, Williams JV. Infectious disease. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 13.
Mitchell AL. Congenital anomalies. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 30.
Sankaran S, Kyle P. Abnormalities of the face and neck. In: Coady AM, Bower S, eds. Twining's Textbook of Fetal Abnormalities. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2015:chap 13.
Review Date: 11/6/2023
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.