Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
Abscesses occur when an area of tissue becomes infected and the body's immune system tries to fight and contain it. White blood cells (WBCs) move through the walls of the blood vessels into the area of the infection and collect in the damaged tissue. During this process, pus forms. Pus is the buildup of fluid, living and dead white blood cells, dead tissue, and bacteria or other foreign substances.
Abscesses can form in almost any part of the body. The skin, under the skin, and the teeth are the most common sites. Abscesses may be caused by bacteria, parasites, and foreign substances.
Abscesses in the skin are easy to see. They are red, raised, and painful. Abscesses in other areas of the body may not be seen, but they may cause organ damage.
Some types and locations of abscesses include:
- Abdominal abscess
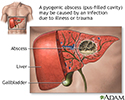
- Amebic liver abscess
- Anorectal abscess
- Bartholin gland abscess
- Brain abscess
- Epidural abscess
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- Spinal cord abscess
- Subcutaneous (skin) abscess
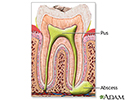
- Tooth abscess
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam, focusing on the symptoms of the abscess.
Tests to locate the abscess include:
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- X-ray (mainly for tooth abscess)
Often, a sample of fluid will be taken from the abscess and tested to see what type of germ is causing the problem.
Treatment
Treatment varies, but often surgery is needed to drain the abscess. Antibiotics can also be used.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you think that you have any type of abscess. Contact your dentist if you think that you have a tooth abscess.
Prevention
Preventing abscesses depends on where they develop. For example, good hygiene can help prevent skin abscesses. Dental hygiene and routine care will prevent tooth abscesses.
References
Ambrose G, Berlin D. Incision and drainage. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts & Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 37.
De Prisco G, Celinski S, Spak CW. Abdominal abscesses and gastrointestinal fistulas. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 29.
Gea-Banacloche JC, Tunkel AR. Brain abscess. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 90.
Pyogenic abscess - illustration
Pyogenic abscess
illustration
Tooth abscess - illustration
Tooth abscess
illustration
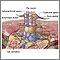
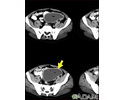
Intra-abdominal abscess - CT scan - illustration
Intra-abdominal abscess - CT scan
illustration
Review Date: 9/10/2022
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.