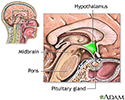
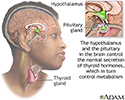
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is an area of the brain that produces hormones that control:
- Body temperature
- Heart rate
- Hunger
- Mood
- Release of hormones from many glands, especially the pituitary gland
- Sex drive
- Sleep
- Thirst
HYPOTHALAMIC DISEASE
Hypothalamic dysfunction can occur as a result of diseases, including:
- Genetic causes (often present at birth or during childhood)
- Infection or inflammation
- Injury as a result of trauma, surgery or radiation
SYMPTOMS OF HYPOTHALAMIC DISEASE
Because the hypothalamus controls so many different functions, hypothalamic disease can have many different symptoms, depending on the cause. The most common symptoms are:
- Increased appetite and rapid weight gain
- Extreme thirst and frequent urination (diabetes insipidus)
- Low body temperature
- Slow heart rate
References
Christian HC. Anatomy and physiology of the hypothalamus and pituitary. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 13.
Myers MG, Olson DP. Neuroendocrine control of energy stores. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 39.
Weiss RE. Neuroendocrinology and the neuroendocrine system. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 210.
Review Date: 5/12/2023
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.