Proctitis
Inflammation - rectum; Rectal inflammation
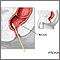
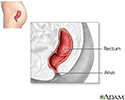
Proctitis is an inflammation of the rectum. It can cause discomfort, bleeding, and the discharge of mucus or pus.
Causes
There are many causes of proctitis. They can be grouped as follows:
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Autoimmune disease
- Harmful substances
- Non-sexually transmitted infection
- Sexually transmitted disease (STD)
Proctitis caused by an STD is common in people who have anal intercourse. STDs that can cause proctitis include gonorrhea, herpes, chlamydia, and lymphogranuloma venereum.
Infections that are not sexually transmitted are less common than STD proctitis. One type of proctitis not from an STD is an infection in children that is caused by the same bacteria as strep throat.
Autoimmune proctitis is linked to diseases such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn disease. If the inflammation is in the rectum only, it may come and go or move upward into the large intestine.
Proctitis may also be caused by some medicines, radiotherapy to prostate or pelvis or inserting harmful substances into the rectum.
Risk factors include:
- Autoimmune disorders, including inflammatory bowel disease
- High-risk sexual practices, such as anal sex
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Bloody stools
- Constipation
- Rectal bleeding
- Rectal discharge, pus
- Rectal pain or discomfort
- Tenesmus (pain with bowel movement)
Exams and Tests
Tests that may be used include:
- Exam of a stool sample
- Proctoscopy
- Rectal culture
- Sigmoidoscopy
Treatment
Most of the time, proctitis will go away when the cause of the problem is treated. Antibiotics are used if an infection is causing the problem.
Corticosteroids or mesalamine suppositories or enemas may relieve symptoms for some people.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is good with treatment.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have symptoms of proctitis.
Prevention
Safe sex practices may help prevent the spread of the disease.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. 2021 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines. www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/proctitis.htm. Reviewed July 22, 2021. Accessed July 18, 2023.
Coates WC. Anorectum. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 82.
Downs JM, Kulow B. Anal diseases. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 129.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases website. Proctitis. www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/proctitis/all-content. Updated December 2021. Accessed July 18, 2023.
Review Date: 5/2/2023
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.