Poison ivy - oak - sumac
Sumac - poisonous; Oak - poisonous; Ivy - poisonous
Poison ivy, oak, or sumac poisoning is an allergic reaction that results from touching the sap of these plants. The sap may be on the plant, in the ashes of burned plants, on an animal, or on other objects that came in contact with the plant, such as clothing, garden tools, and sports equipment.
Small amounts of sap can remain under a person's fingernails for several days. It must be purposely removed with thorough cleaning.
Plants in this family are strong and hard to get rid of. They are found in every state of the continental United States. These plants grow best along cool streams and lakes. They grow especially well in areas that are sunny and hot. They do not survive well above 1,500 m (5,000 feet), in deserts, or in rainforests.
This article is for information only. DO NOT use it to treat or manage an actual poison exposure. If you or someone you are with has an exposure, call your local emergency number (such as 911), or your local poison control center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States.
Poisonous Ingredient
One poisonous ingredient is the chemical urushiol.
Where Found
The poisonous ingredient can be found in:
- Bruised roots, stems, flowers, leaves, fruit
- Pollen, oil, and resin of poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac
Note: This list may not be all-inclusive.
Symptoms
Symptoms of exposure may include:
- Blisters
- Burning skin
- Itching
- Redness of the skin
- Swelling
In addition to the skin, symptoms can affect the eyes and mouth.
The rash may be spread by touching undried sap and moving it around the skin.
The oil can also stick to animal fur, which explains why people often contract the skin irritation (dermatitis) from their outdoor pets.
Home Care
Carefully remove any contaminated clothing, being careful not to spread the oils from the plant.
Wash the area right away with soap of any type and water. Quickly washing the area can prevent a reaction. However, it most often does not help if done more than 1 hour after touching the plant's sap. Flush the eyes out with water for at least 15 minutes. Take care to clean under the fingernails well to remove traces of toxin.
Carefully wash any contaminated objects or clothing alone in hot soapy water. DO NOT let the items touch any other clothing or materials.
An over-the-counter steroid cream may help relieve itching. Over the counter antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may be used, but are of limited benefit. Make sure to read the label to determine if it is safe for you to take an antihistamine, since this type of drug may interact with other medicines you're taking.
Before Calling Emergency
Get the following information:
- Person's age, weight, and condition
- Name of the plant, if known
- Amount swallowed (if swallowed)
Poison Control
Your local poison control center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States. This national hotline will let you talk to experts in poisoning. They will give you further instructions.
This is a free and confidential service. All local poison control centers in the United States use this national number. You should call if you have any questions about poisoning or poison prevention. It does not need to be an emergency. You can call for any reason, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
What to Expect at the Emergency Room
Unless the reaction is severe, the person will probably not need to visit the emergency room. If you are concerned, contact your health care provider or poison control.
At the provider's office, the person may receive:
- Antihistamine or steroids by mouth or applied to the skin
- Washing of the skin (irrigation)
Take a sample of the plant with you to the doctor or hospital, if possible.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Life-threatening reactions may occur if the poisonous ingredients are swallowed or are breathed in (which can happen when the plants are burned).
Typical skin rashes most often go away without any long-term problems. A skin infection may develop if the affected areas are not kept clean.
Wear protective clothing whenever possible when travelling through areas where these plants grow. DO NOT touch or eat any unfamiliar plant. Wash your hands after working in the garden or walking in the woods.
References
American Academy of Dermatology Association website. Poison ivy, oak, and sumac: how to treat the rash. www.aad.org/public/everyday-care/itchy-skin/poison-ivy/treat-rash. Accessed December 4, 2023.
Buttaravoli PM, Leffler S, Herrington RR. Toxicodendron (rhus) allergic contact dermatitis: (poison ivy, oak, or sumac). In: Buttaravoli P, Leffler SM, Herrington RR, eds. Minor Emergencies. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 184.
Dinulos JGH. Contact dermatitis and patch testing. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 4.
Freeman EE, Paul S, Shofner JD, Kimball AB. Plant-induced dermatitis. In: Auerbach PS, Cushing TA, Harris NS, eds. Auerbach's Wilderness Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 64.
McGovern TW. Dermatoses due to plants. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 17.
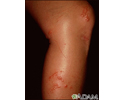
Poison oak rash on the arm - illustration
Poison oak rash on the arm
illustration
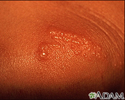
Poison ivy on the knee - illustration
Poison ivy on the knee
illustration
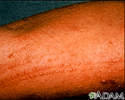
Poison ivy on the leg - illustration
Poison ivy on the leg
illustration
Review Date: 11/2/2023
Reviewed By: Jesse Borke, MD, CPE, FAAEM, FACEP, Attending Physician at Kaiser Permanente, Orange County, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.