Breath odor
Bad breath; Halitosis; Malodor; Fetor oris; Fetor ex ore; Fetor ex oris; Breath malodor; Oral malodor
Breath odor is the scent of the air you breathe out of your mouth. Unpleasant breath odor is commonly called bad breath.
Considerations
Bad breath is usually related to poor dental hygiene. Not brushing and flossing regularly causes sulfur compounds to be released by bacteria in the mouth.
Some disorders will produce distinct breath odors. Some examples are:
- A fruity odor to the breath is a sign of ketoacidosis, which may occur in diabetes. It is a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Breath that smells like feces can occur with prolonged vomiting, especially when there is a bowel obstruction. It may also occur temporarily if a person has a tube placed through the nose or mouth to drain their stomach.
- The breath may have an ammonia-like odor (also described as urine-like or "fishy") in people with chronic kidney failure.
Causes
Bad breath may be caused by:
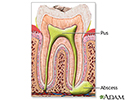
- Abscessed tooth
- Gum surgery
- Alcoholism
- Cavities
- Dentures
- Eating certain foods, such as cabbage, garlic, or raw onions
- Coffee and poorly pH-balanced diet
- Object stuck in the nose (usually happens in kids); often a white, yellow, or bloody discharge from one nostril
- Gum disease (gingivitis, gingivostomatitis, acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG)
- Impacted tooth
- Poor dental hygiene
- Tonsils with deep crypts and sulfur granules
- Sinus infection
- Throat infection
- Tobacco smoking
- Vitamin supplements (especially in large doses)
- Some medicines, including insulin shots, triamterene, and paraldehyde
Some diseases that may cause unpleasant breath odor are:
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG)
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative mucositis
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Acute renal failure
- Bowel obstruction
- Bronchiectasis
- Chronic kidney failure
- Esophageal cancer
- Gastric carcinoma
- Gastrojejunocolic fistula
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Lung infection or abscess
- Ozena, or atrophic rhinitis
- Periodontal disease
- Pharyngitis
- Zenker diverticulum
Home Care
Use proper dental hygiene, especially flossing. Remember that mouthwashes are not effective in treating the underlying problem.
Fresh parsley or a strong mint is often an effective way to fight temporary bad breath. Avoid smoking.
Otherwise, follow your health care provider's instructions to treat any underlying cause of bad breath.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- Breath odor does not go away and there is not an obvious cause (such as smoking or eating foods that cause the odor).
- You have breath odor and signs of a respiratory infection, such as fever, cough, or face pain with discharge from your nose.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take a medical history and perform a physical exam.
You may be asked the following medical history questions:
- Is there a specific odor (such as fish, ammonia, fruit, feces, or alcohol)?
- Have you recently eaten a spicy meal, garlic, cabbage, or other "odorous" food?
- Do you take vitamin supplements?
- Do you smoke?
- What home care and oral hygiene measures have you tried? How effective are they?
- Have you had a recent sore throat, sinus infection, tooth abscess, or other illness?
- What other symptoms do you have?
The physical exam will include a thorough inspection of your mouth and nose. A throat culture may be taken if you have a sore throat or mouth sores.
In rare cases, tests that may be performed include:
- Blood tests to check for diabetes or kidney failure
- Endoscopy (EGD)
- X-ray of the abdomen
- X-ray of the chest
Antibiotics may be prescribed for some conditions. For an object in the nose, your provider will use an instrument to remove it.
References
Murr AH, Pletcher SD. Approach to the patient with nose, sinus, and ear disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 394.
Teughels W, Dadamio J, Robben J, Dekeyser C, Quirynen M. Halitosis (breath malodor). In: Newman MG, Klokkevold PR, Elangovan S, Hernandez-Kapila YL, eds. Newman and Carranza's Clinical Periodontology and Implantology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 31.
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Michael Kapner, DDS, General Dentistry, Norwalk Medical Center, Norwalk CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.