Mycoplasma pneumonia
Walking pneumonia; Community-acquired pneumonia - mycoplasma; Community-acquired pneumonia - atypical
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ.
Mycoplasma pneumonia is caused by the bacteria Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M pneumoniae).
This type of pneumonia is also called atypical pneumonia because the symptoms are different from those of pneumonia due to other common bacteria.

Causes
Mycoplasma pneumonia usually affects people younger than 40.
People who live or work in crowded areas such as schools and homeless shelters have a higher chance of getting this condition. But many people who get sick with it have no known risk factors.
Symptoms
Symptoms are often mild and appear over 1 to 3 weeks. They may become more severe in some people.
Common symptoms include any of the following:
- Chest pain
- Chills
- Cough, usually dry and not bloody
- Excessive sweating
- Fever (may be high)
- Headache
- Sore throat
Less common symptoms include:
- Ear pain
- Eye pain or soreness
- Muscle aches and joint stiffness
- Neck lump
- Rapid breathing
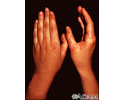
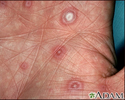
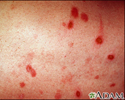
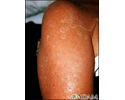
- Skin lesions or rash
Exams and Tests
People with suspected pneumonia should have a complete medical evaluation. It may be hard for your health care provider to tell whether you have pneumonia, bronchitis, or another respiratory infection, so you may need a chest x-ray.
Depending on how severe your symptoms are, other tests may be done, including:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Blood tests
- Bronchoscopy in which a flexible tube with a lighted camera on the end is passed down to your lungs in selected cases (rarely needed)
- CT scan of the chest
- Measuring levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood (arterial blood gases)
- Nose or throat swab to check for bacteria and viruses
- Open lung biopsy (only done in very serious illnesses when the diagnosis cannot be made from other sources, so very rarely needed)
- Sputum tests to check for mycoplasma bacteria
In many cases, it is not necessary to make the specific diagnosis before starting treatment.
Treatment
To feel better, you can take these self-care measures at home:
- Control your fever with aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen), or acetaminophen. Do not give aspirin to children because it may cause a dangerous illness called Reye syndrome.
- Do not take cough medicines without first contacting your provider. Cough medicines may make it harder for your body to cough up the extra sputum.
- Drink plenty of fluids to help loosen secretions and bring up phlegm.
- Get a lot of rest. Have someone else do household chores.
Antibiotics are used to treat atypical pneumonia:
- You may be able to take antibiotics by mouth at home.
- If your condition is severe, you will likely be admitted to a hospital. There, you will be given antibiotics through a vein (intravenously), as well as oxygen.
- Antibiotics are usually prescribed for 3 to 5 days, although sometimes they may be used for 2 weeks or more.
- Finish all the antibiotics you've been prescribed, even if you feel better. If you stop the medicine too soon, the pneumonia can return and may be harder to treat.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people recover completely without antibiotics, although antibiotics may speed recovery. In untreated adults, cough and weakness can last for up to a month. The disease can be more serious in older adults and in those with a weakened immune system.
Possible Complications
Complications that may result include any of the following:
- Ear inflammation called bullous myringitis
- Hemolytic anemia, a condition in which there are not enough red blood cells in the blood because the body is destroying them
- Skin rashes
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop a fever, cough, or shortness of breath. There are many causes for these symptoms. The provider will need to check for pneumonia.
Also, contact your provider if you have been diagnosed with this type of pneumonia and your symptoms become worse after improving first.
Prevention
Wash your hands often, and have other people around you do the same.
Avoid contact with other sick people.
If your immune system is weak, stay away from crowds. Ask visitors who have a cold to wear a mask.
Do not smoke. If you do, get help to quit.
Get the appropriate vaccines like the flu and COVID-19 shots as prescribed. Ask your provider if you should get a pneumococcal vaccine (pneumonia vaccine).
References
Dockrell DH, Ho A, Gordon SB. Community-acquired pneumonia. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46.
Goldman DL. Mycoplasma infections. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 293.
Holzman RS, Simberkoff MS, Leaf HL. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and atypical pneumonia. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 183.
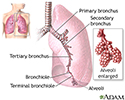
Lungs - illustration
Lungs
illustration
Erythema multiforme, circular lesions - hands - illustration
Erythema multiforme, circular lesions - hands
illustration
Erythema multiforme, target lesions on the palm - illustration
Erythema multiforme, target lesions on the palm
illustration
Erythema multiforme on the leg - illustration
Erythema multiforme on the leg
illustration
Exfoliation following erythroderma - illustration
Exfoliation following erythroderma
illustration
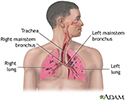
Respiratory system - illustration
Respiratory system
illustration
Review Date: 8/19/2024