Pneumonia in adults - discharge
Bronchopneumonia adults - discharge; Lung infection adults - discharge
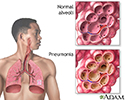
You have pneumonia, which is an infection in your lungs. Now that you are going home, it is important to follow your health care provider's instructions on taking care of yourself at home. Use the information below as a reminder.
When You're in the Hospital
In the hospital, your providers helped you breathe better. They also gave you medicine to help your body get rid of the germs that cause pneumonia. They also made sure you got enough liquids and nutrients.
What to Expect at Home
You will still have symptoms of pneumonia after you leave the hospital.
- Your cough will slowly get better over 7 to 14 days.
- Sleeping and eating may take up to a week to return to normal.
- Your energy level may take 2 weeks or more to return to normal.
You will need to take time off work. For a while, you might not be able to do other things that you are used to doing.
Self-care
Breathing warm, moist air helps loosen the sticky mucus that may make you feel like you are choking. Other things that may also help include:
- Placing a warm, wet washcloth loosely near your nose and mouth.
- Filling a humidifier with warm water and breathing in the warm mist.
Coughing helps clear your airways. Take a couple of deep breaths, 2 to 3 times every hour. Deep breaths help open up your lungs.
While lying down, tap your chest gently a few times a day. This helps bring up mucus from the lungs.
If you smoke, now is the time to quit. Do not allow smoking in your home.
Drink plenty of liquids, as long as your provider says it is OK.
- Drink water, juice, or weak tea.
- Drink at least 6 to 10 cups (1.4 to 2.4 liters) a day.
- Do not drink alcohol.
Get plenty of rest when you go home. If you have trouble sleeping at night, take naps during the day.
Medicines
Your provider may prescribe antibiotics for you. These are medicines that kill the germs that cause pneumonia. Antibiotics help most people with pneumonia get better. Do not miss any doses. Take the full duration of the prescription medicine, even if you start to feel better.
Do not take cough or cold medicines unless your provider says it is OK. Coughing helps your body get rid of mucus from your lungs.
Your provider will tell you if it is OK to use acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil or Motrin) for fever or pain. If these medicines are OK to use, your provider will tell you how much to take and how often to take them.
Avoid Infections
To prevent pneumonia in the future:
- Get a flu (influenza) shot every year.
- Ask your provider if you need to get the pneumococcal (pneumonia) vaccine.
- Get a COVID-19 vaccine on the recommended schedule.
- Wash your hands often.
- Stay away from crowds.
- Ask visitors who have a cold to wear a mask.
Going Home With Oxygen
Your provider may prescribe oxygen for you to use at home. Oxygen helps you breathe better.
- Never change how much oxygen is flowing without asking your provider.
- Always have a back-up supply of oxygen at home or with you when you go out.
- Keep the phone number of your oxygen supplier with you at all times.
- Learn how to use oxygen safely at home.
- Never smoke near an oxygen tank.
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your provider or call 911 or the local emergency number if your breathing is:
- Getting harder
- Faster than before
- Shallow and you cannot get a deep breath
Also contact your provider or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have any of the following:
- Need to lean forward when sitting to breathe more easily
- Have chest pain when you take a deep breath
- Headaches more often than usual
- Feel sleepy or confused
- Fever returns
- Coughing up dark mucus or blood
- Fingertips or the skin around your fingernails is blue
References
Ellison RT, Donowitz GR. Acute pneumonia. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 67.
File TM. Streptococcus pneumoniae pulmonary infections. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 268.
Review Date: 3/16/2024
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.