Premenstrual breast changes
Premenstrual tenderness and swelling of the breasts; Breast tenderness - premenstrual; Breast swelling - premenstrual
Premenstrual swelling and tenderness of both breasts often occurs during the second half of the menstrual cycle.
Considerations
Symptoms of premenstrual breast tenderness may range from mild to severe. Symptoms usually:
- Are most severe just before each menstrual period
- Improve during or right after the menstrual period
Breast tissue may have a dense, bumpy, "cobblestone" feel to the fingers. This feel is usually more in the outer areas, particularly near the armpit. There may also be an off and on or ongoing sense of breast fullness with dull, heavy pain, and tenderness.
Causes
Hormone changes during the menstrual cycle may lead to breast swelling. More estrogen is made early in the cycle and it peaks just before mid-cycle. This causes the breast ducts to grow in size. The progesterone level peaks near the 21st day (in a 28-day cycle). This causes growth of the breast lobules (milk glands).
Premenstrual breast swelling is often linked with:
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- Fibrocystic breast disease (benign breast changes)
Premenstrual breast tenderness and swelling probably occur to some degree in nearly all women. More severe symptoms may occur in many women during their childbearing years. Symptoms may be less in women taking birth control pills.
Risk factors may include:
- Family history
- High-fat diet
- Too much caffeine
Home Care
Self-care tips:
- Eat a lower fat diet.
- Avoid caffeine (coffee, tea, and chocolate).
- Avoid salt 1 to 2 weeks before your period starts.
- Get moderate to vigorous exercise every day.
- Wear a well-fitting bra day and night to provide good breast support.
You should practice breast awareness. Do check your breasts for changes at regular intervals.
The effectiveness of vitamin E, vitamin B6, and herbal preparations such as evening primrose oil are somewhat controversial. This should be discussed with your health care provider.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you:
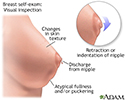
- Have new, unusual, or changing lumps in your breast tissue
- Have one-sided (unilateral) lumps in your breast tissue
- Do not know how to properly perform breast self-examination
- Are a woman, age 40 years or older, and have never had a screening mammogram
- Have discharge from your nipple, particularly if it is a bloody or brown discharge
- Have symptoms that interfere with your ability to sleep, and diet changes and exercise have not helped
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take your medical history and do a physical examination. The provider will check for breast lumps, and will note the qualities of the lump (firm, soft, smooth, bumpy, and so on).
A mammogram or breast ultrasound may be done. These tests will evaluate any abnormal finding on a breast exam. If a lump is found that is not clearly benign, you may need a breast biopsy.
These medicines from your provider may reduce or eliminate symptoms:
- Injections or shots that contain the hormone progestin (Depoprovera). A single shot works for up to 90 days. These injections are given into the muscles of the upper arm or buttocks. They relieve symptoms by stopping menstrual periods.
- Birth control pills.
- Diuretics (water pills) taken before your menstrual period. These pills may reduce breast swelling and tenderness.
- Danazol may be used in severe cases. Danazol is a synthetic (manmade) androgen (male hormone). If this does not work for you, other medicines may be prescribed.
References
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists website. Dysmenorrhea: painful periods. www.acog.org/patient-resources/faqs/gynecologic-problems/dysmenorrhea-painful-periods. Updated January 2022. Accessed April 25, 2024.
Cox DM, Lippe C, Geletzke AK, et al. Etiology and management of benign breast disease. In: Klimberg VS, Gradishar WJ, Bland KI, Korourian S, White J, Copeland EM, eds. Bland and Copeland's The Breast: Comprehensive Management of Benign and Malignant Diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 14.
Expert Panel on Breast Imaging; Holbrook AI, Moy L, Akin EA, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria breast pain. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(11S):S276-S282. PMID: 30392596 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30392596/.
Mendiratta V, Lentz GM. Primary and secondary dysmenorrhea, premenstrual syndrome, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder: etiology, diagnosis, management. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 35.
Sandadi S, Rock DT, Orr JW, Valea FA. Breast diseases: detection, management, and surveillance of breast disease. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 15.
Breast self-exam
Animation
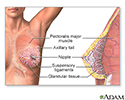
Female Breast - illustration
Female Breast
illustration
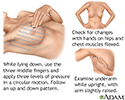
Breast self-exam - illustration
Breast self-exam
illustration
Breast self-exam - illustration
Breast self-exam
illustration
Review Date: 4/16/2024
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.