Obstructive uropathy
Uropathy - obstructive
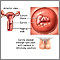
Obstructive uropathy is a condition in which the flow of urine is blocked. This causes the urine to back up and injure one or both kidneys.
Causes
Obstructive uropathy occurs when urine cannot drain through the urinary tract. Urine backs up into the kidneys and may cause them to become swollen. This condition is known as hydronephrosis.
Obstructive uropathy can affect one or both kidneys. It can occur suddenly or be a long-term problem.
Common causes of obstructive uropathy include:
- Bladder stones
- Kidney stones
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate)
- Advanced prostate cancer
- Bladder or ureteral cancer
- Bladder prolapse (also called dropped bladder)
- Colon cancer
- Cervical or uterine cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Any cancer that spreads
- Scar tissue that occurs inside or outside of the ureters
- Scar tissue that occurs inside the urethra
- Problems with the nerves that supply the bladder
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on whether the problem starts slowly or suddenly and if one or both kidneys are involved. Symptoms may include:
- Mild to severe pain in the flank. The pain may be felt on one or both sides.
- Fever.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Weight gain or swelling (edema) of kidney.
You may also have problems passing urine, such as:
- Urge to urinate often
- Decrease in the force of urine stream or difficulty urinating
- Dribbling of urine
- Not feeling as if the bladder is emptied
- Need to urinate more often at night
- Decreased amount of urine
- Leakage of urine (urinary incontinence)
- Blood in urine
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will order functional or imaging studies to detect obstructive uropathy. Commonly used tests include:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, abdomen, or pelvis
- CT scan of the kidneys, abdomen, or pelvis
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
- Voiding cystourethrogram
- Renal nuclear scan
- MRI of the abdomen or pelvis
- Urodynamic test
- Cystoscopy
Treatment
Medicines may be used if the cause is an enlarged prostate.
Stents or drains placed in the ureter or in a part of the kidney called the renal pelvis may provide short-term relief of symptoms.
Nephrostomy tubes, which drain urine from the kidneys through the back, may be used to bypass the blockage.
A Foley catheter placed through the urethra into the bladder may also help urine flow.
Short-term relief from the blockage is possible without surgery. However, the cause of the blockage must be removed and the urinary system repaired. Surgery may be needed for long-term relief from the problem.
The kidney may need to be removed if the blockage causes severe loss of function.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If the blockage comes on suddenly, kidney damage is less likely if the problem is detected and treated right away. Often, the damage to the kidneys goes away. Long-term damage to the kidneys may occur if the blockage has been present for a long time.
If only one kidney is damaged, chronic kidney problems are less likely.
You may need dialysis or a kidney transplant if there is damage to both kidneys and they do not function, even after the blockage is repaired.
Possible Complications
Obstructive uropathy can cause permanent and severe damage to the kidneys, resulting in kidney failure.
If the problem was caused by a blockage in the bladder, the bladder may have long-term damage. This may lead to problems emptying the bladder or leakage of urine.
Obstructive uropathy is linked to higher chances of urinary tract infections.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of obstructive uropathy.
Prevention
Obstructive uropathy can be prevented by treating disorders that can cause it.
References
Frøkiaer J. Urinary tract obstruction. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 37.
Gallagher KM, Hughes J. Urinary tract obstruction. In: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Tonelli M eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 61.
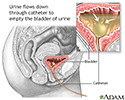
Bladder catheterization - female - illustration
Bladder catheterization - female
illustration
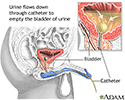
Bladder catheterization - male - illustration
Bladder catheterization - male
illustration
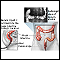
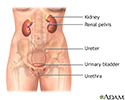
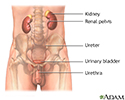
Female urinary tract - illustration
Female urinary tract
illustration
Male urinary tract - illustration
Male urinary tract
illustration
Bladder catheterization - female - illustration
Bladder catheterization - female
illustration
Bladder catheterization - male - illustration
Bladder catheterization - male
illustration
Female urinary tract - illustration
Female urinary tract
illustration
Male urinary tract - illustration
Male urinary tract
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Sovrin M. Shah, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.