Lyme disease blood test
Lyme disease serology; ELISA for Lyme disease; Western blot for Lyme disease
The Lyme disease blood test looks for antibodies in the blood to the bacteria that causes Lyme disease. The test is used to help diagnose Lyme disease.
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
A laboratory specialist looks for Lyme disease antibodies in the blood sample using the ELISA test. If the ELISA test is positive, it must be confirmed with another test called the Western blot test.
How to Prepare for the Test
You do not need to take special steps to prepare for this test.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is done to check for the diagnosis of Lyme disease.
Normal Results
A negative test result is normal. This means none or few antibodies to Lyme disease were seen in your blood sample. If the ELISA test is negative, usually no other testing is needed.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive ELISA result is abnormal. This means antibodies were seen in your blood sample. But, this does not confirm a diagnosis of Lyme disease. A positive ELISA result must be followed up with a Western blot test. Only a positive Western blot test can confirm the diagnosis of Lyme disease.
For many people, the ELISA test remains positive, even after they have been treated for Lyme disease and no longer have symptoms.
A positive ELISA test may also occur with certain diseases not related to Lyme disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight but may include:
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
- Excessive bleeding
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Nikolic D. Spirochete infections. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 61.
Steere AC. Lyme disease (Lyme borreliosis) due to Borrelia burgdorferi. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 241.
Lyme disease
Animation
Blood test - illustration
Blood test
illustration
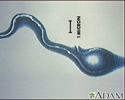
Lyme disease organism, Borrelia burgdorferi - illustration
Lyme disease organism, Borrelia burgdorferi
illustration
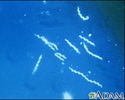
Deer ticks - illustration
Deer ticks
illustration
Ticks - illustration
Ticks
illustration
Lyme disease - Borrelia burgdorferi organism - illustration
Lyme disease - Borrelia burgdorferi organism
illustration
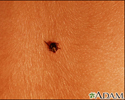
Tick imbedded in the skin - illustration
Tick imbedded in the skin
illustration
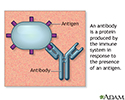
Antibodies - illustration
Antibodies
illustration
Blood test - illustration
Blood test
illustration
Lyme disease organism, Borrelia burgdorferi - illustration
Lyme disease organism, Borrelia burgdorferi
illustration
Deer ticks - illustration
Deer ticks
illustration
Ticks - illustration
Ticks
illustration
Lyme disease - Borrelia burgdorferi organism - illustration
Lyme disease - Borrelia burgdorferi organism
illustration
Tick imbedded in the skin - illustration
Tick imbedded in the skin
illustration
Antibodies - illustration
Antibodies
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.